A 36-year-old man presented to the emergency room with fever and fatigue for two weeks. Analytically showed: hemoglobin 143 g/L, platelet count 218 × 109/L, leukocytosis 17.5 × 109/L with lymphocytosis (81%), alanine aminotransferase 3.22 µkat/L, aspartate aminotransferase 2.13 µkat/L, lactate dehydrogenase 7.15 µkat/L, serologic testing for hepatitis B, C and HIV negative. Monospot test was positive.
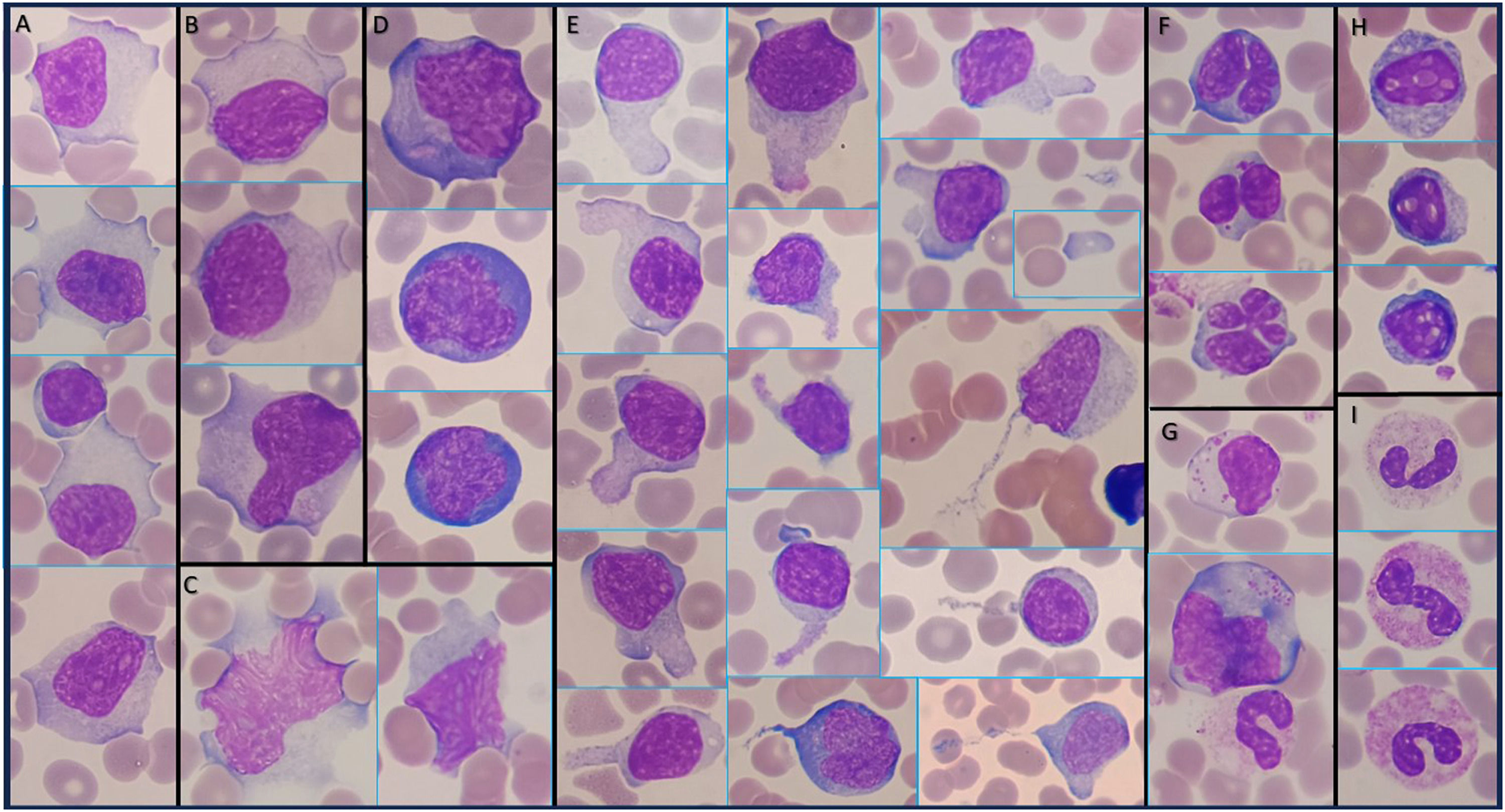
The peripheral blood film (PBF) showed atypical lymphocytes (21% of leukocytes): (a) large lymphocytes with abundant and indented cytoplasm that surrounds red blood cells, with large nucleus some having central nucleoli; (b) sometimes with an apparent double cytoplasmic membrane; (c) large lymphocytes with a diffuse and reticular chromatin pattern and diffuse reticular cytoplasm; (d) large lymphocytes with strongly basophilic cytoplasm (plasmacytoid lymphocytes); (e) large to medium lymphocytes with large, medium and small uropods (thick and thin), some presenting microspikes or detached cytoplasm (hand-mirror cells); (f) medium to small lymphocytes with lobulated nucleus, sometimes occasionally resembling a cloverleaf; (g) large to medium granular lymphocytes; (h) apoptotic lymphocytes with regular vacuolated nucleus, and (i) band forms or hyposegmented neutrophils (pseudo-Pelger-Huët) with toxic granulations (Figure 1, Wright-Giemsa stain, × 100 objective).
Infectious mononucleosis (IM) is associated with primary infection by Epstein–Barr virus (EBV), a gamma herpesvirus. The incubation period is about 30–50 days. 1
Atypical lymphocytes are activated T lymphocytes produced as part of the immunological response to EBV infected B lymphocytes. The presence of (a) ≥50 % lymphocytes in total leukocytes, and (b) ≥10 % atypical lymphocytes on PBF (sensitivity 75 %; specificity 92 %) are strongly suggestive of IM. 1,2
A positive heterophile antibody test (monospot) has a sensitivity of 85 % and a specificity 94 %. 1
Aminotransferase levels may be elevated in adults. 1
The diagnosis of IM can be done by clinical presentation, the presence of atypical lymphocytes on a PBF, and a positive monospot. 1
If the diagnosis is unclear, EBV-specific serologic testing (testing for specific IgM and IgG antibodies against viral capsid antigens, early antigens, and EBV nuclear antigen proteins) can be used to a final diagnose. 1
Treatment is supportive. Antiviral therapy is not recommended, and corticosteroids are only recommended for complicated cases. 1
Data availability statementData sharing is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Ethics of approval statementGranted an ethical approval by the Ethical Commission of CAML.
Patient consent statementNot applicable.
Permission to reproduce material from other sourcesNot applicable.
Clinical trial registrationNot applicable.
Author contributionsMarco P. Barros Pinto: performed the research, analysed data and wrote the paper.
Funding statementNone.