Severe congenital neutropenia is a rare disease, and autosomal dominantly inherited. ELANE mutation is the most frequently observed genetic defect in the registries from North America and Western Europe. However, in eastern countries where consanguineous marriages are common, autosomal recessive forms might be more frequent.
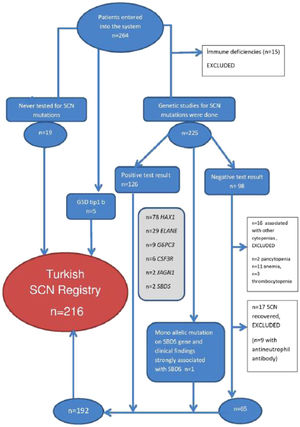
Two hundred and sixteen patients with severe congenital neutropenia from 28 different pediatric centers in Turkey were registered. Patients inclusion and exclusion strategies apre shown in Figure-1.
The most frequently observed mutation was HAX1 mutation (n = 78, 36.1%). A heterozygous ELANE mutation was detected in 29 patients (13.4%) in our cohort. Biallelic mutations of G6PC3 (n = 9, 4.3%), CSF3R (n = 6, 2.9%), and JAGN1 (n = 2, 1%) were also observed (Table 1). Eighty seven percent of HAX1 mutations were detected in the same point of p.W44X. There were 6 patients who had a HAX1 mutation other than c.130-131 pW44X point mutation. Four had novel mutations. The novel mutations were detected in 7 ELANE patients. Interestingly 2 out of 4 patients with CSF3R mutation and 4 out of 9 patients with G6PC3 had a novel mutation.
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor treatment was given to 174 patients (80.6%). Two patients died with infectious complications, and five patients developed myelodysplastic syndrome/acute myeloblastic leukemia (Table 2). The mean (± mean standard error) follow-up period was 129.7 ± 76.3 months, and overall survival was 96.8% (CI, 94.4-99.1%) at the age of 15 years.
Clinical features and characteristics of the patients who developed MDS/AML
In Turkey, mutation analysis should be started with HAX1, and if this is negative, ELANE and G6PC3 should be checked. Because of the very high percentage of consanguineous marriage, rare mutations should be tested in patients with a negative mutation screen.