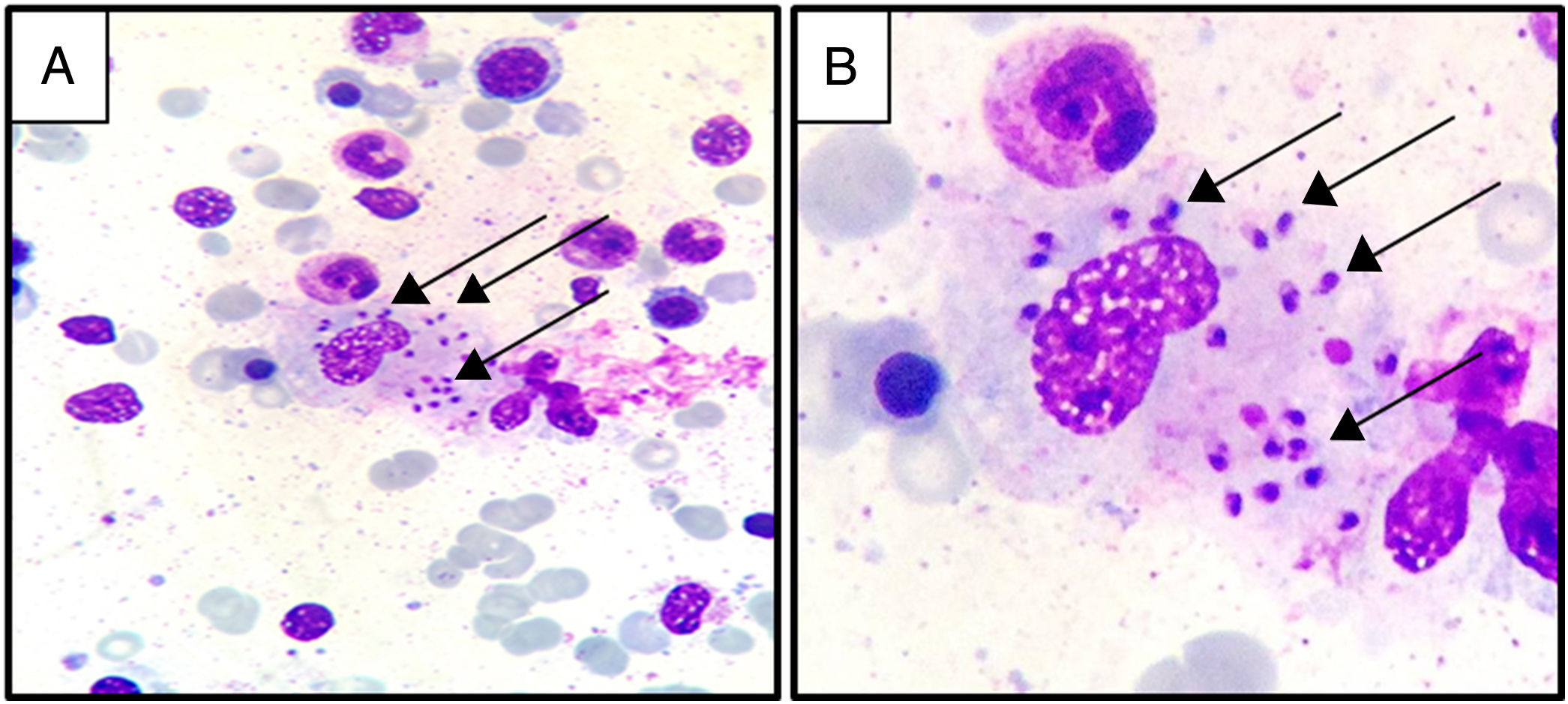
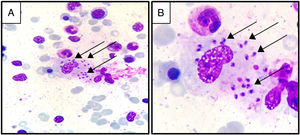
A 50-year-old man came to the emergency room of a university hospital complaining of weight loss, fever and abdominal pain associated with hepatosplenomegaly. Laboratory investigations revealed pancytopenia with red blood cell (RBC) count of 2.35×1012/L, hemoglobin 7.2g/dL (RBCs with rouleaux formation), platelets of 75.7×109/L, white blood cell count of 2.77×109/L (with 58% neutrophils, 27% lymphocytes, 15% monocytes, 0% eosinophils and 0% basophils), hypoalbuminemia (1.31g/dL) and hypergammaglobulinemia (6.63g/dL). Serological test results were negative for antibodies for hepatitis (B and C) and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Due to the laboratory findings and sustained pancytopenia, a bone marrow biopsy was performed which showed Leishmania amastigotes phagocytosed by macrophages (Figure 1) confirming the diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis infection.1,2
The Impact Factor measures the average number of citations received in a particular year by papers published in the journal during the two preceding years.
© Clarivate Analytics, Journal Citation Reports 2025
SRJ is a prestige metric based on the idea that not all citations are the same. SJR uses a similar algorithm as the Google page rank; it provides a quantitative and qualitative measure of the journal's impact.
See moreSNIP measures contextual citation impact by wighting citations based on the total number of citations in a subject field.
See more