X Eurasian Hematology Oncology Congress
More infoPolymyxins are bactericidal drugs that bind to lipopolysaccharides (LPS) and phospholipids in the outer cell membrane of gram-negative bacteria (1,2). The most important side effect of intravenous polymyxins is nephrotoxicity, neurotoxicity. Hypersensitivity reactions including rash, itching, urticaria, and fever have also been reported. It can also cause skin hyperpigmentation (3,4,5). We will present the rash thought to have developed due to polymyxin in an elderly patient diagnosed with AML.
Case reportA 77-year-old male patient diagnosed with AML was admitted to the hospital for a chemotherapy session. After the initial examination, he was hospitalized due to complaints of dyspnea, weakness, and cough. Polymyxin B was started upon recommendation to the patient, who was consulted with the department of chest diseases and infectious diseases regarding his current infection status.
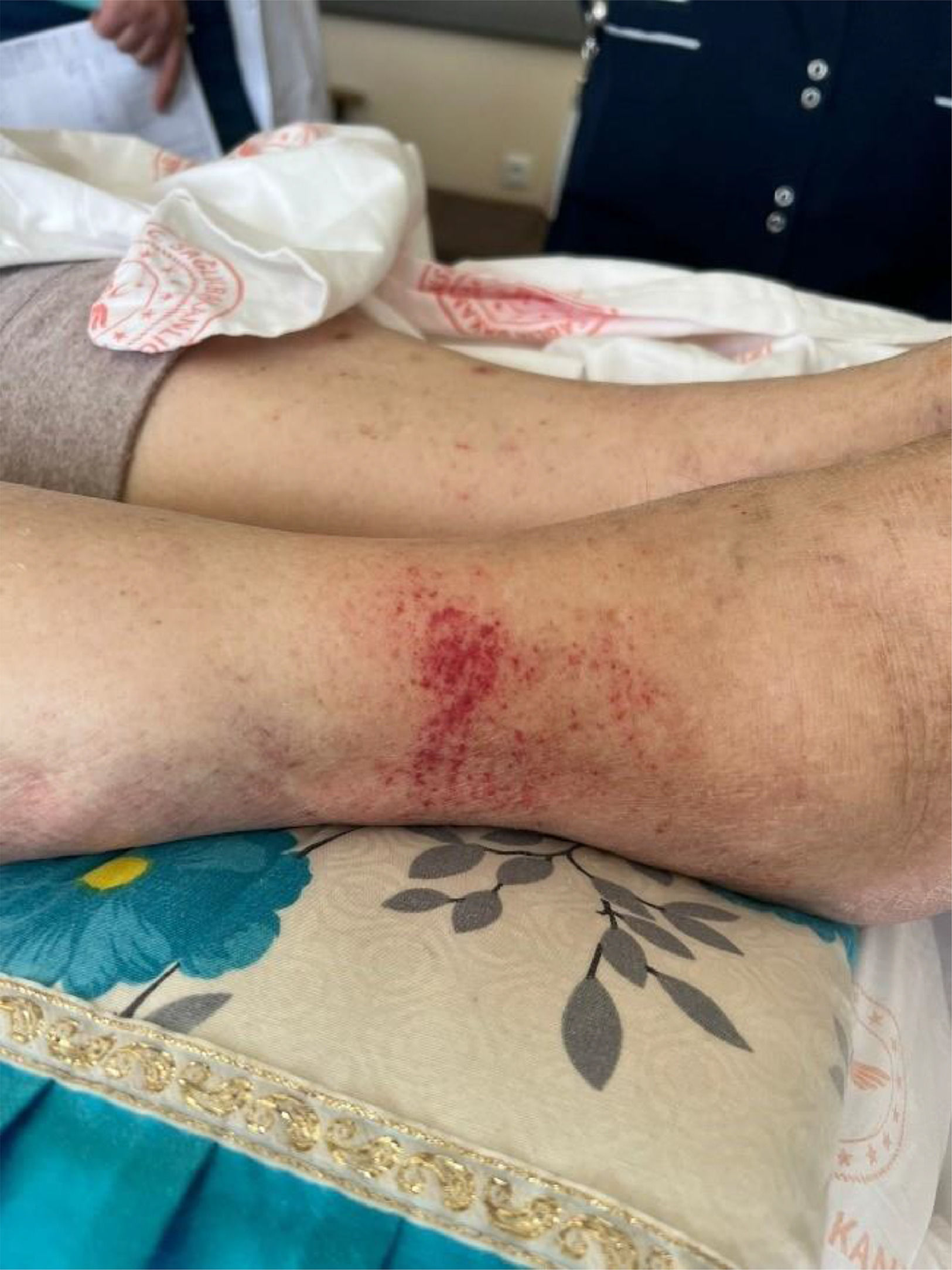
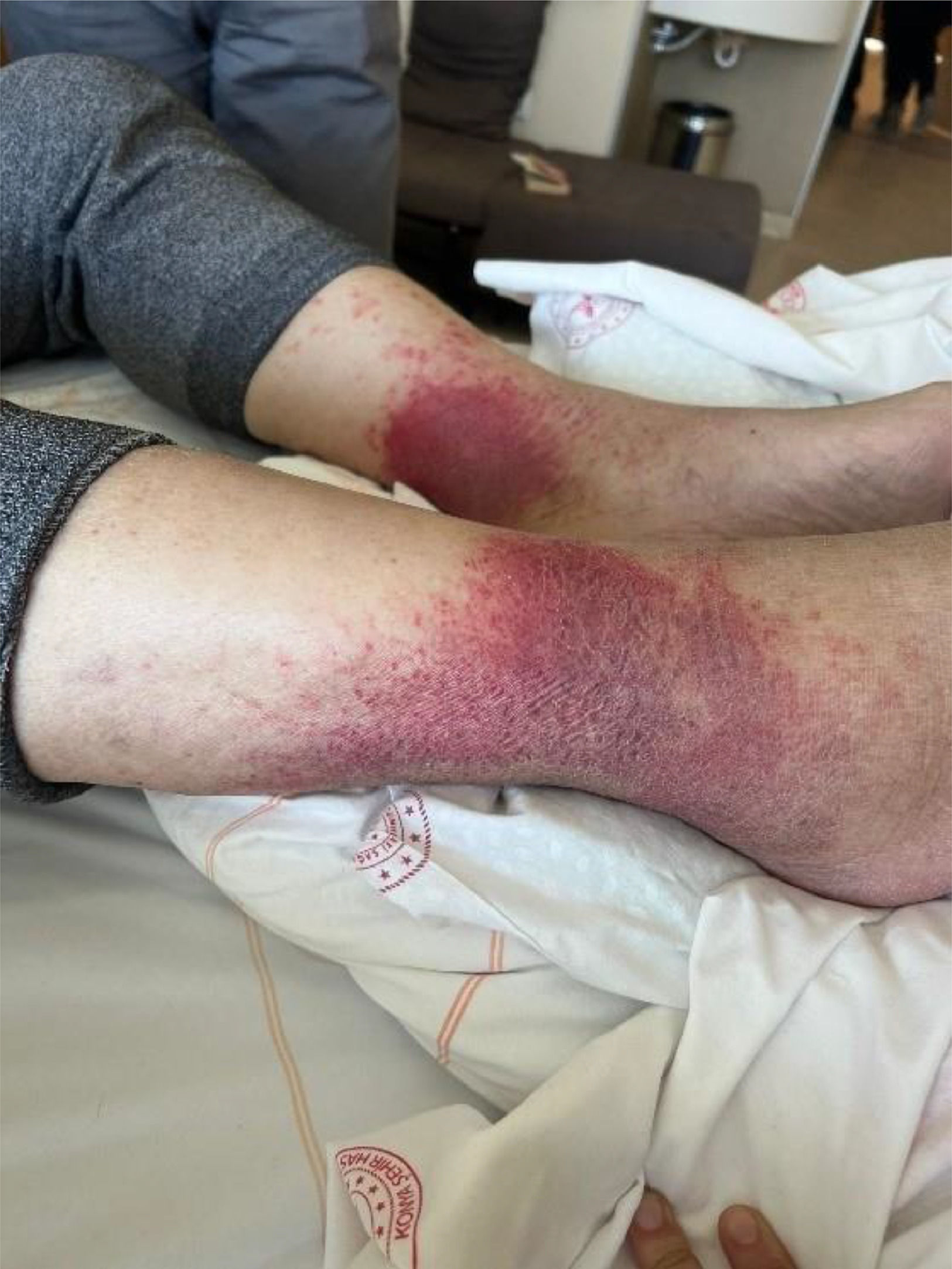
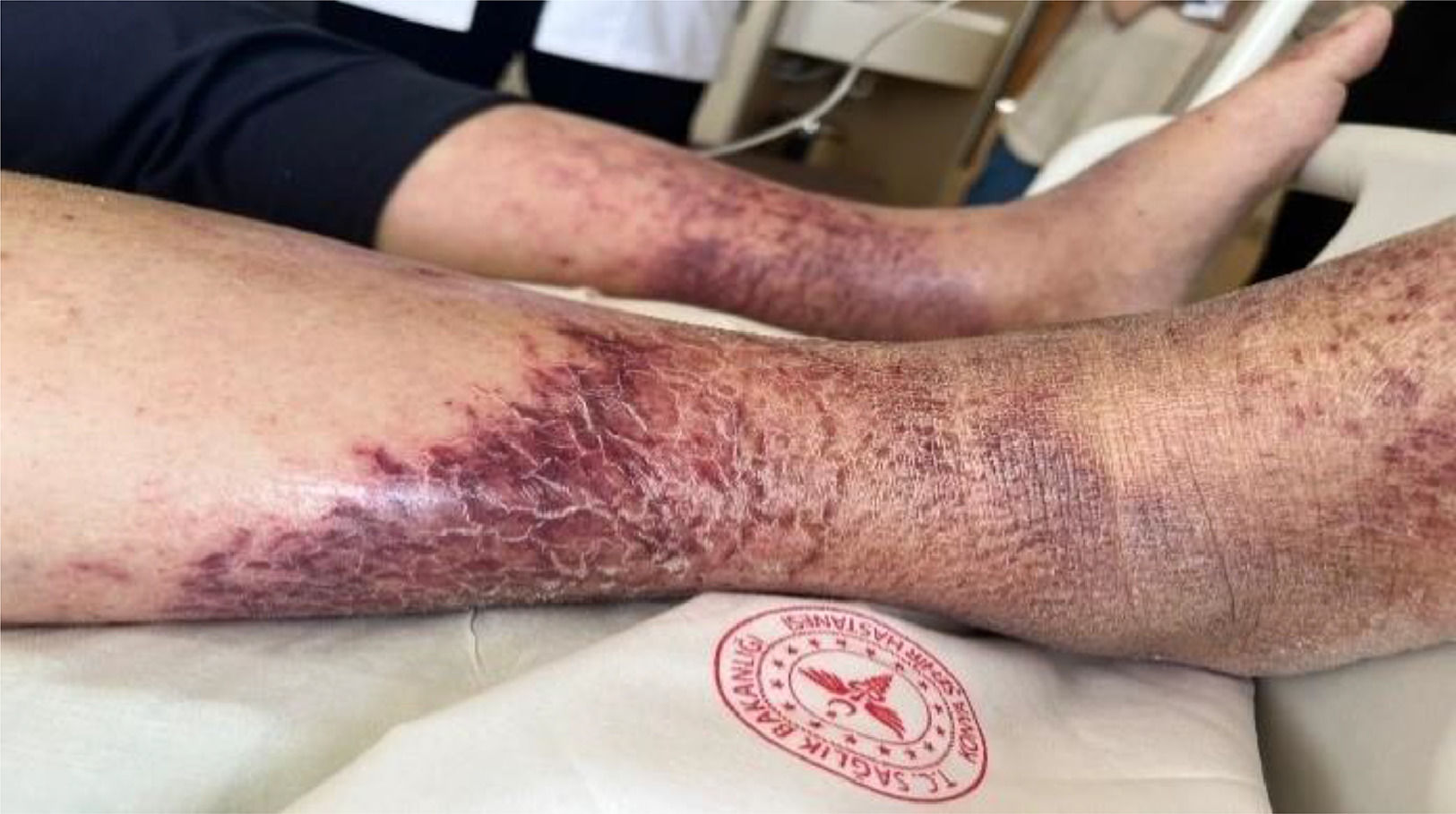
Results: During the follow-up, petechial rashes and itching began to occur on both lower legs, starting from the ankle and spreading upwards, and it was noted that the rash and itching occurred after the use of polymyxin B. After the suspected drug was discontinued, the itching gradually decreased, and the rash was observed to become widespread and change color. The patient's rashes were photographed, and his follow-up continued and after comleting the treatment he was discharged.
ConclusionIn this multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria era, the use of polymyxines has spread. Due to the use of these agents, adverse events such as pruritus, maculapapular rashes, and urticaria may occur (6). Patients should be observed for hypersensitivity reactions related to polymyxin B use, and the cause of these symptoms should be enlightened with the right anamnesis.