Multiple myeloma is a plasma cell neoplasm with acquired genetic abnormalities of clinical and prognostic importance. Multiple myeloma differs from other hematologic malignancies due to a high fraction of low proliferating malignant plasma cells and the paucity of plasma cells in bone marrow aspiration samples, making cytogenetic analysis a challenge. An abnormal karyotype is found in only one-third of patients with multiple myeloma and interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization is the most useful test for studying the chromosomal abnormalities present in almost 90% of cases. However, it is necessary to study the genetic abnormalities in plasma cells after their identification or selection by morphology, immunophenotyping or sorting. Other challenges are the selection of the most informative FISH panel and determining cut-off levels for FISH probes. This study reports the validation of interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization using CD138 positive cells, according to proposed guidelines published by the European Myeloma Network (EMN) in 2012.
MethodBone marrow samples from patients with multiple myeloma were used to standardize a panel of five probes [1q amplification, 13q14 deletion, 17p deletion, t(4;14), and t(14;16)] in CD138+ cells purified by magnetic cell sorting.
ResultsThis test was validated with a low turnaround time and good reproducibility. Five of six samples showed genetic abnormalities. Monosomy/deletion 13 plus t(4;14) were found in two cases.
ConclusionThis technique together with magnetic cell sorting is effective and can be used in the routine laboratory practice. In addition, magnetic cell sorting provides a pure plasma cell population that allows other molecular and genomic studies.
Multiple myeloma (MM) is a disease characterized by clonal proliferation of plasma cells (PCs) in bone marrow, which leads to bone marrow failure, skeletal lesions, suppression of normal immunoglobulin synthesis and production of a monoclonal protein.1 This disease accounts for between 10% and 15% of hematological cancers. The median age at diagnosis is 60 years, and the evolution is heterogeneous, with the survival time varying from a few months to more than a decade.2,3
MM shows acquired genetic abnormalities of clinical importance. In about half of the cases, the initial genetic process involves a reciprocal translocation between the immunoglobulin heavy (IgH) gene (14q32) and many target genes including CCND1 (11q13), FGFR3/MMSET (4p16) and MAF (16q23).4,5
The study of cytogenetic abnormalities by karyotyping is limited because of the low mitotic index of the malignant PCs.6–8 Only 20–50% of the cases show clonal abnormalities by G banding karyotype. However, the presence of hypodiploidy or monosomy of chromosome 13 predicts poor survival.9–13
Molecular studies show that most MM cases present genetic abnormalities with interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization (iFISH) being the most useful cytogenetic tool for their investigation.7,14,15 However, iFISH testing requires previous identification or selection of PCs by morphology, immunophenotyping or sorting. Cell selection using the anti-CD138 antibody can be performed using magnetic columns or sorting. The major limitation of this approach is the considerable loss of cells during the purification process. In the cytoplasmic immunoglobulin (Clg) fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) technique, PC detection is carried out using fluorescent anti-Kappa or anti-Lambda antibodies in the PC cytoplasm and analysis is performed only using this population.4,5,16
The other challenges in MM testing with FISH are probe selection, the determination of cut-off levels and number of PCs to be scored. The European Myeloma Network (EMN) has organized two workshops on iFISH in MM. In 2012, they published some technical recommendations herein transcribed from the paper:
- (1)
Material should be part of the first draw of the aspirate;
- (2)
Samples should be sent at suitable times to allow for the lengthy processing procedure;
- (3)
Most importantly, PCs must be purified or specifically identified;
- (4)
Cut-off levels should be relatively conservative: 10% for fusion or breakapart probes, and 20% for numerical abnormalities;
- (5)
Informative probes should be combined for best effect;
- (6)
In specialist laboratories, a single experienced analyst is considered adequate;
- (7)
At least 100 PCs should be scored;
- (8)
Essential abnormalities to test for are t(4;14), t(14;16) and 17p13 deletions;
- (9)
Suitable commercial probes should be available for clinically relevant abnormalities;
- (10)
The clinical report should be expressed clearly and must state the percentage of PC involved and the method used for identification”.4
This study aimed to standardize an iFISH panel test for MM for its incorporation in laboratories as a routine cytogenetic test.
MethodsThis research was evaluated by the Ethics Committee of the Hospital (SGPP number 169913 – “Validation of laboratory tests for Clinical Pathology Laboratory”). The study was conducted in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration as revised in 2008.
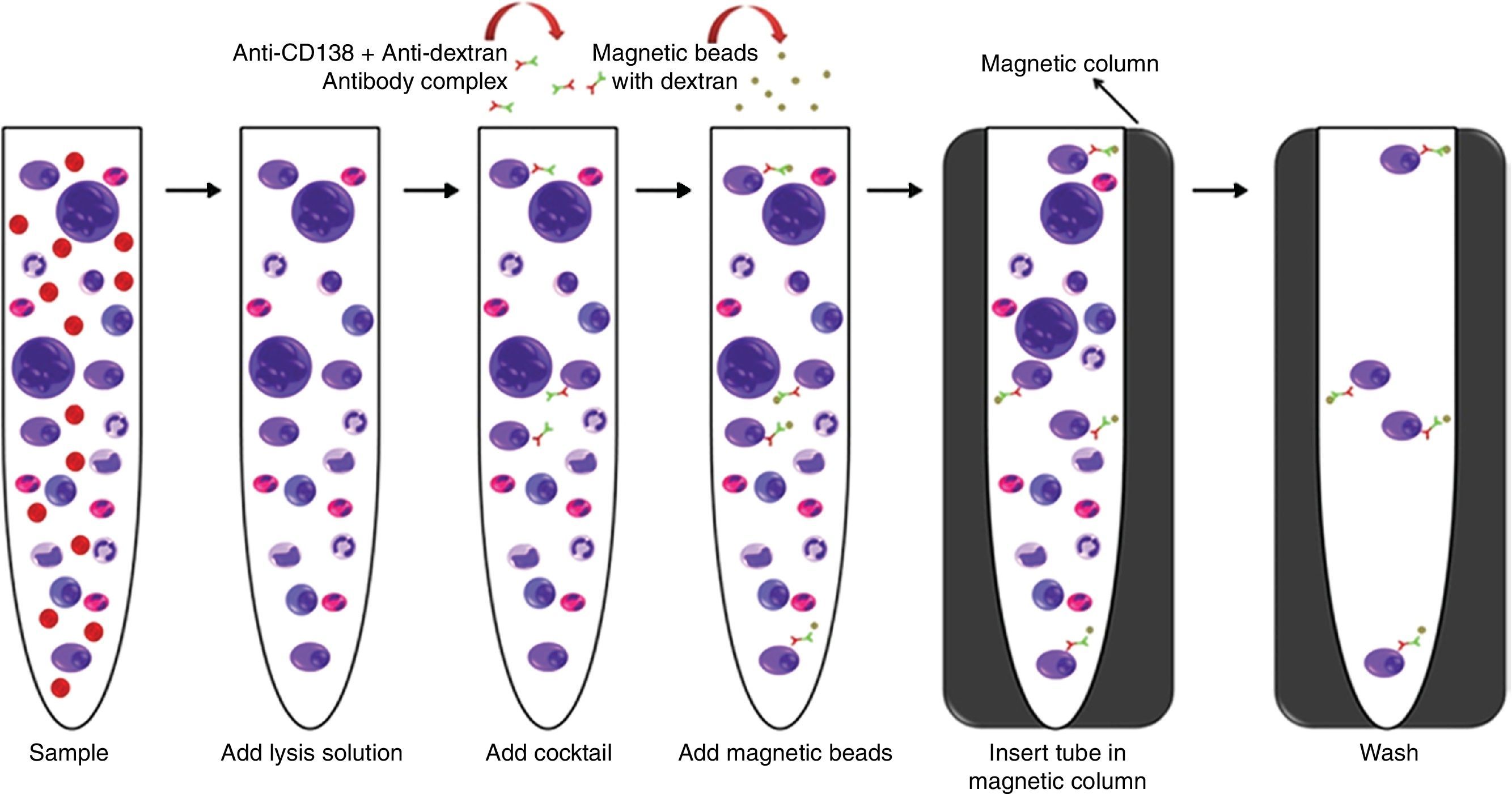
Twelve bone marrow samples from patients diagnosed with MM received at the Cytogenetic Laboratory of a private Hospital in Sao Paulo from March to October 2014 were selected for this validation. The process is described in Figures 1–5.
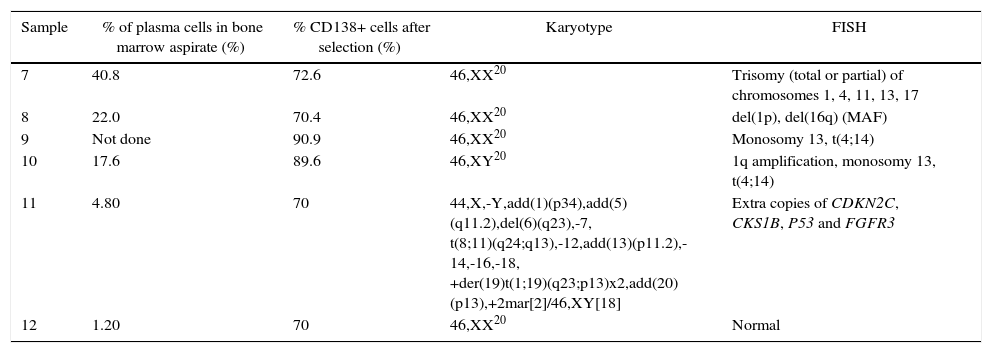
This first step was performed using the “EasySep™ Human WB”, “BM CD138 Positive Selection Cocktail” and “EasySep™ Whole Blood Magnetic Particles” (Stemcell Technologies™) kits.
The process started less than 12h after the sample was collected, at room temperature following the manufacturers’ protocol. At the end of the process, the tube was removed from the magnetic column and the selected material was re-suspended in 200μL of washed solution, which was used after this step for flow cytometry analysis and the harvest procedure (Figure 1).
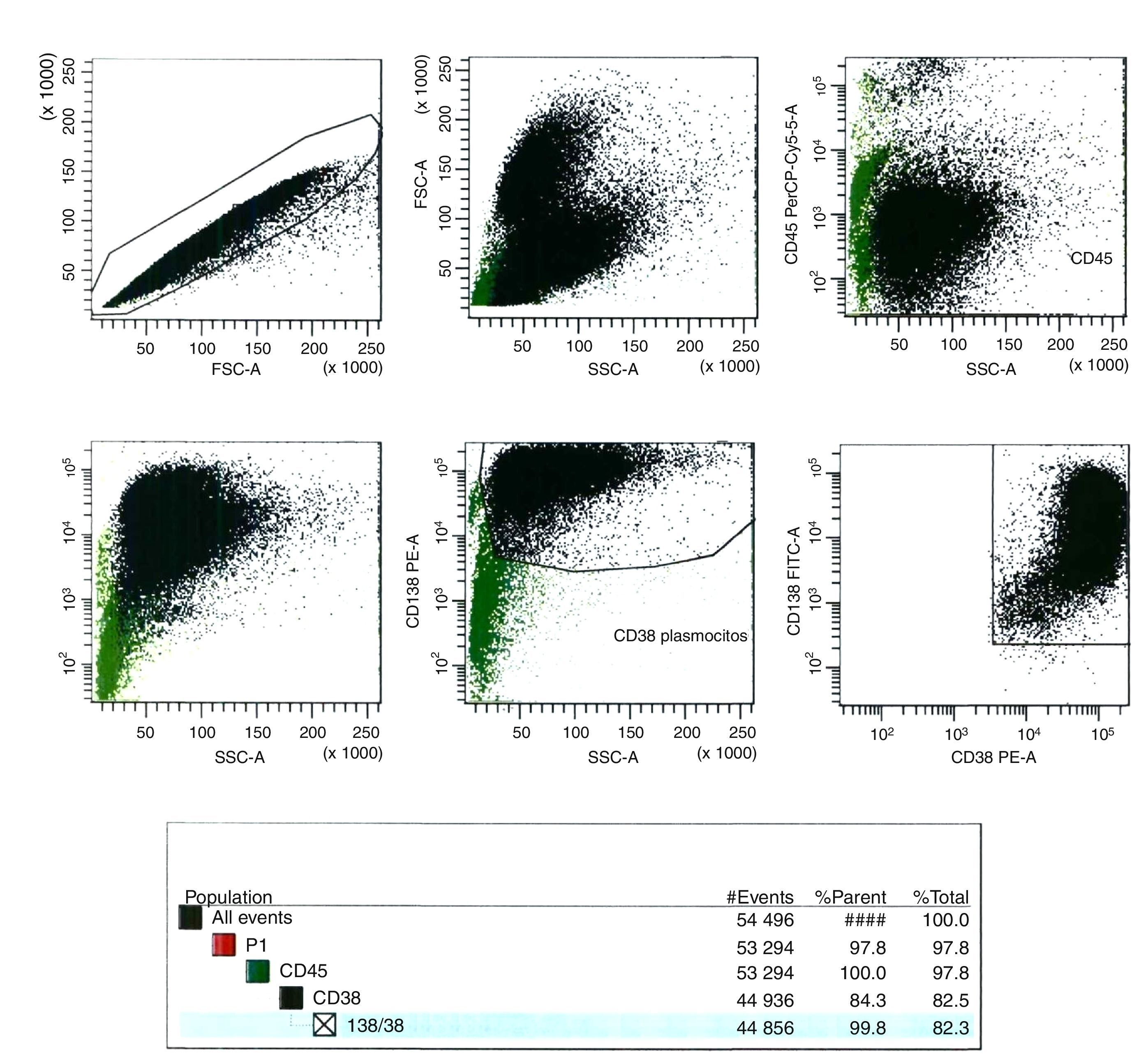
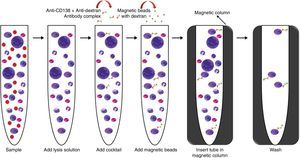
Flow cytometry analysis of magnetic cell sorting enrichmentAt least 100 cells (counted in a Neubauer chamber) of the magnetic cell sorting (MACS) enrichment sample were evaluated by flow cytometry. Anti-CD138-FTIC (B-A38 clone, Exbio), anti-CD38-PE (T16 clone, Immunotech) and anti-CD45-PE-Cy5 (J33 clone, Immunotech) monoclonal antibodies (MoAb) were used to identify bone marrow PCs. Flow analysis was carried out in FACS CantoII equipment (Becton, Dickinson and Company). Data analysis was performed using the BD FACS Diva software (Becton, Dickinson and Company, version 6.1.3, USA) (Figure 2).
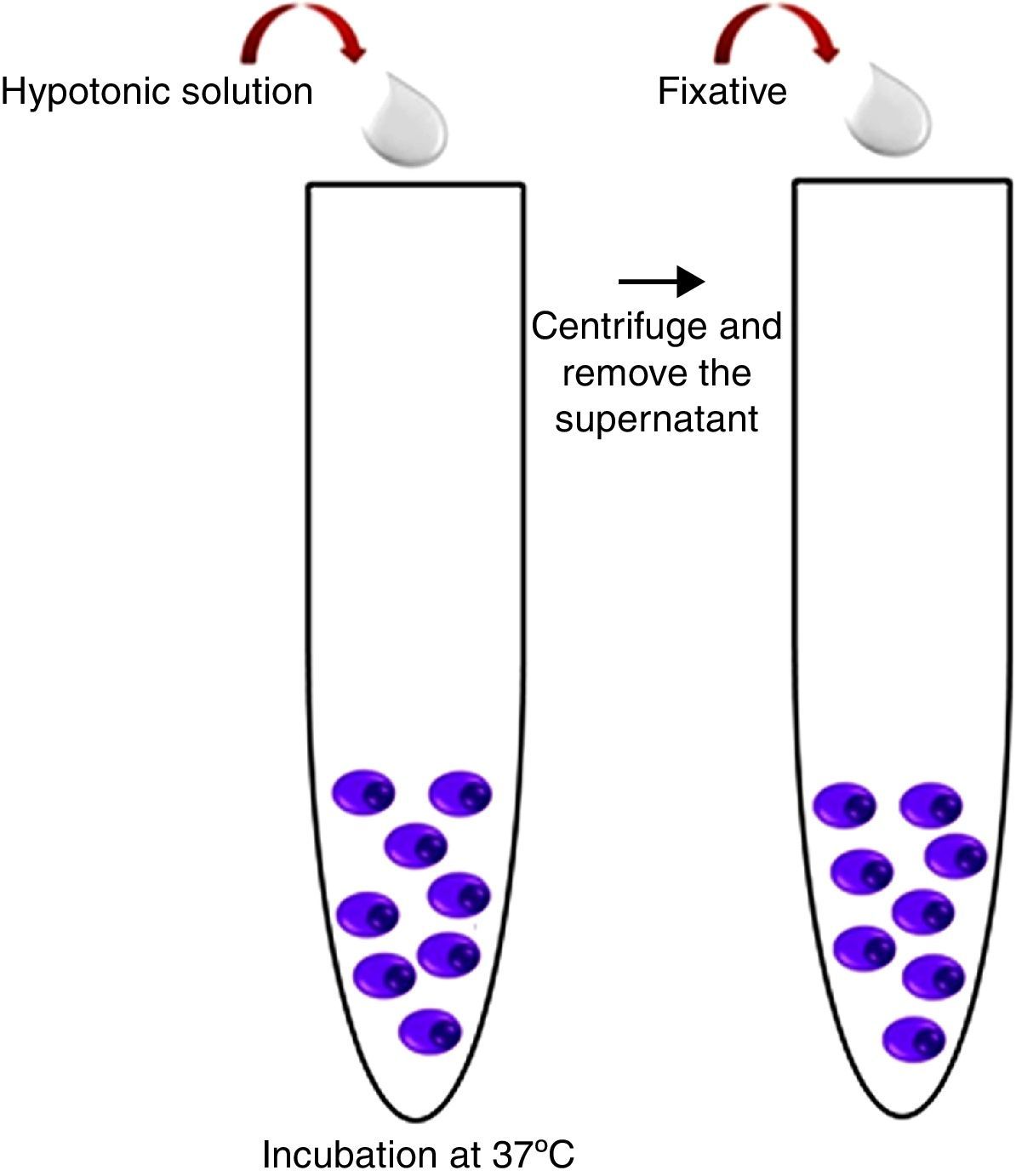
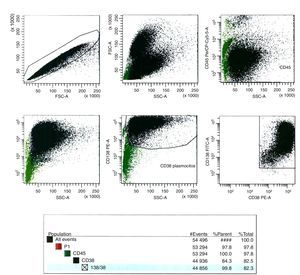
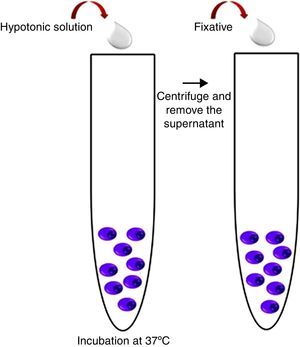
Harvest procedureThree milliliters of hypotonic potassium chloride solution (KCl – 0.075mol/L) were added to the MACS enrichment sample and incubated for 16min at 37°C. After this time, 1mL of fixative solution (Carnoy's solution: 3:1 methanol/acetic acid) was added and the tube was centrifuged at 1500rpm for 8min. The supernatant was discarded; material was re-suspended in 3mL of Carnoy's solution and centrifuged again at 1500rpm for 8min. The latter procedure was repeated two more times and the resulting pellet was used in the iFISH procedure (Figure 3).
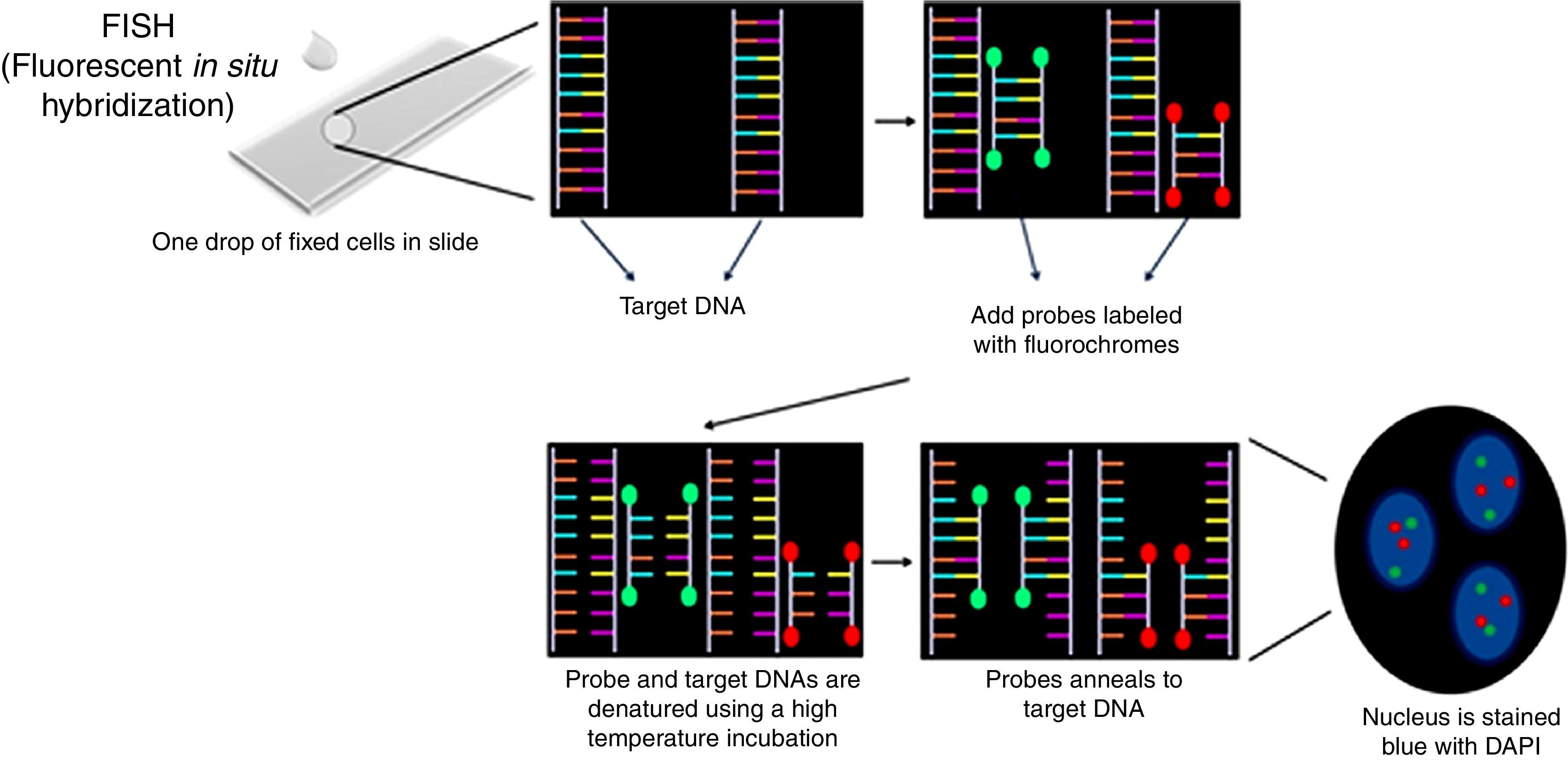
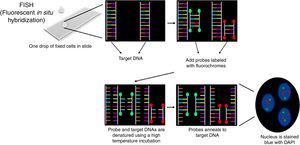
Interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization procedureThe pellet obtained in the last step was re-suspended in 600–1000μL of Carnoy's solution and centrifuged in a Cytospin centrifuge at 1000rpm for 5min (100–200μL of the material for each slide). According to the manufactures’ protocol, slides were pretreated in the following solutions: 2× SSC, 70% ethanol, 85% ethanol and 100% ethanol for 2min at room temperature. Ten microliters of Cytocell Aquarius® probe was applied on a slide and coverslipped. This was done with each different probe. Co-denaturation of the probe and target DNA was performed on a hot plate at 75°C for 5min. Slides were incubated for 12–16h in a humid chamber for hybridization and then were washed in 0.4× SSC solution at 42°C for 2min followed by a second wash (2× SSC+0.1% NP40) at room temperature for 1min. Nuclei were counterstained with 10μL of DAPI II (Cytocell Aquarius®) and coverslipped. Slides were stored at 4°C for 10min (Figure 4).
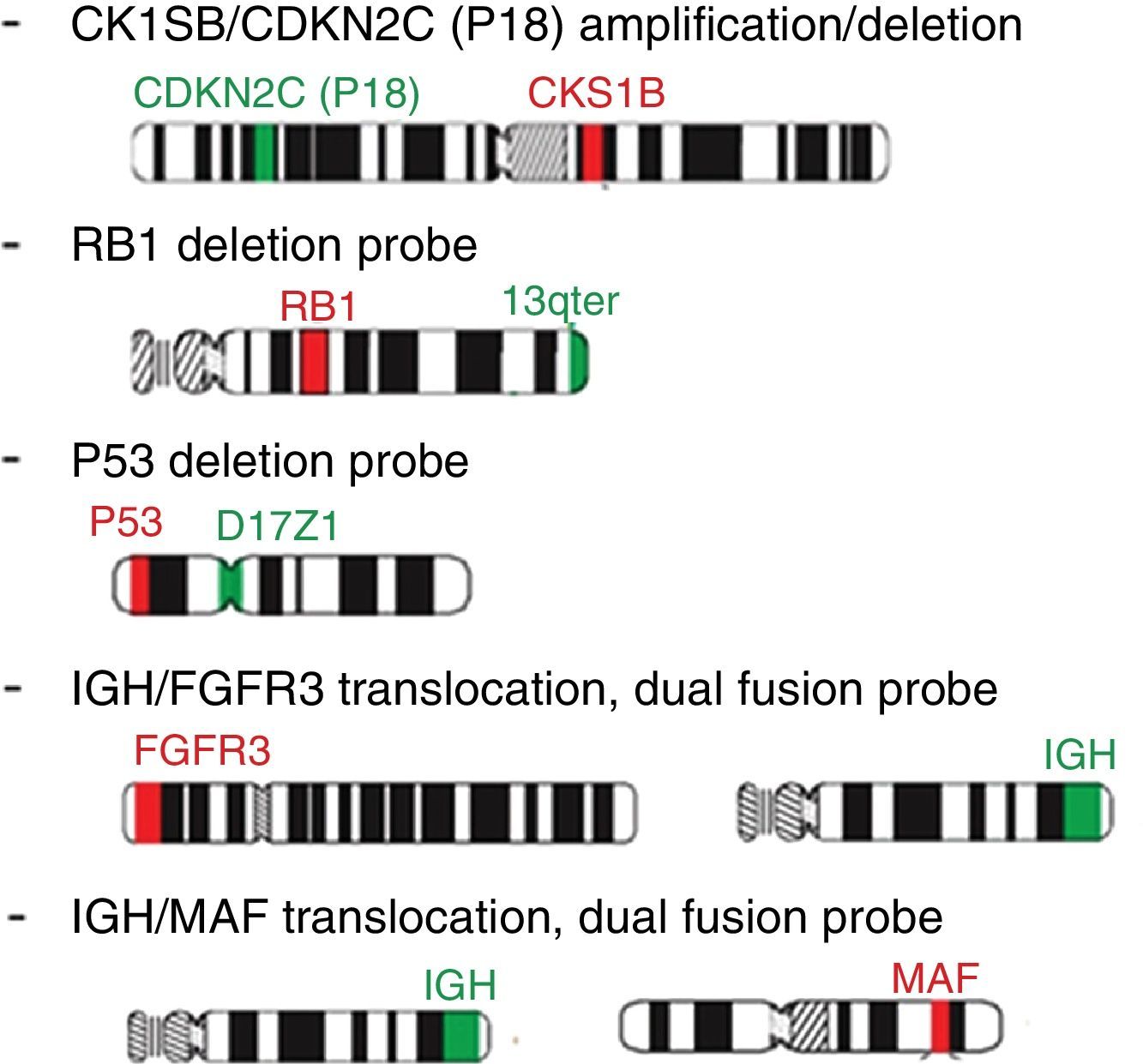
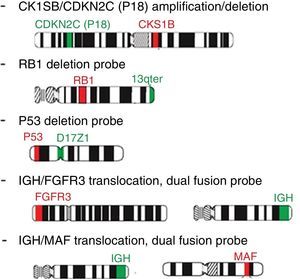
Probe panel selection and scoringFive probes (Cytocell Aquarius®) were selected: Amplification 1q dual color; Deletion 13q (RB1) dual color; Deletion 17p13.1 (P53) dual color; t(4;14) IGH/FGFR3 dual color, dual fusion and t(14;16) IGH/MAF dual color, dual fusion. iFISH analysis of probe hybridization was performed with a 100× objective fluorescence microscope (Zeiss, Germany) with single and triple emission filters. Images were captured using Isis software (Zeiss, version 5.4.9, Germany). All slides were evaluated by two technicians (50 interphase nuclei each), totaling 100 cells. In case of discrepant results, the analysis of another 50 cells was carried out by a third technician (Figure 5).
Determination of the cut-off pointsThe EMN cut-off level recommendation was followed: 10% for fusion and breakapart probes and 20% for numerical aberrations.
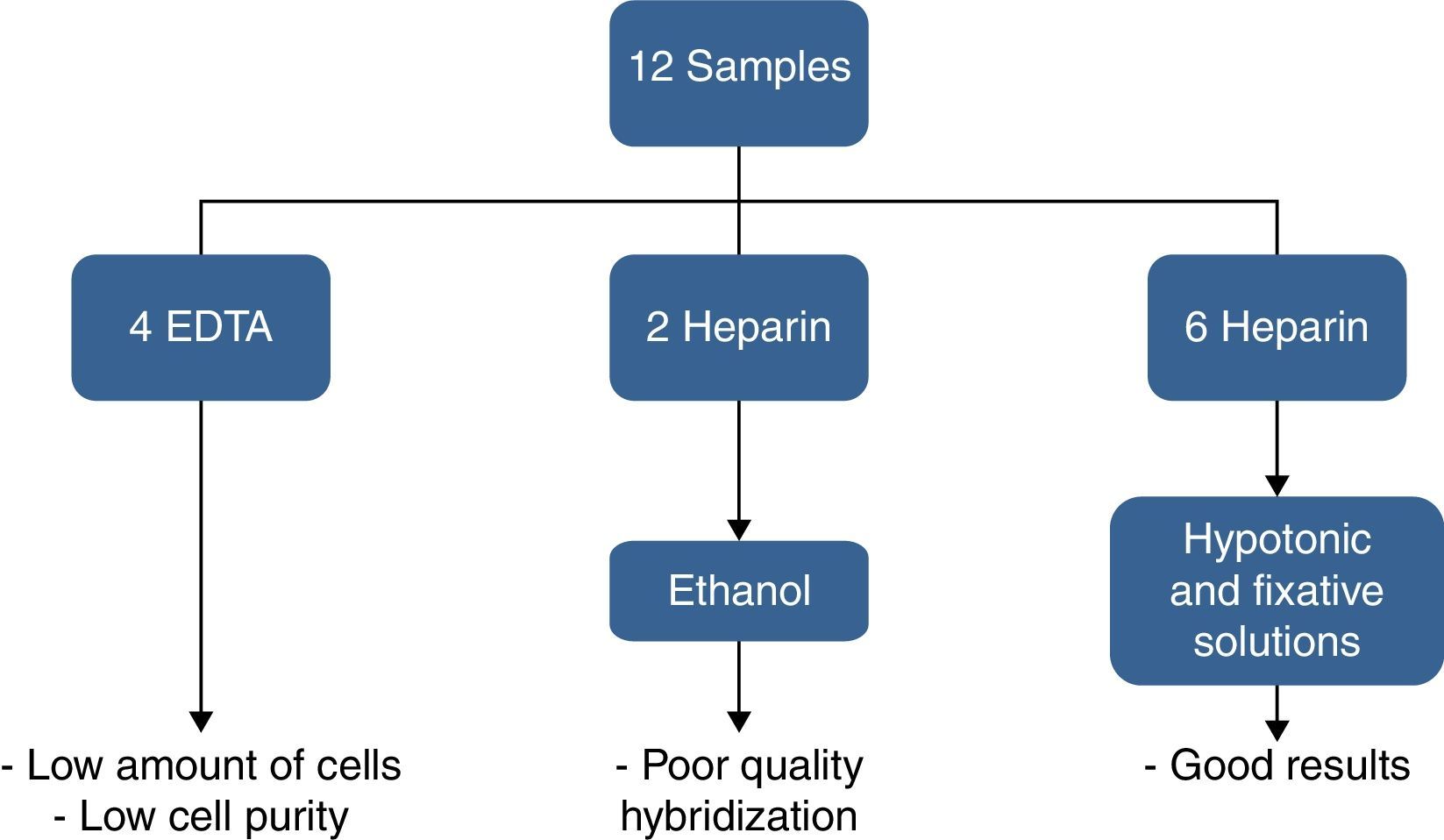
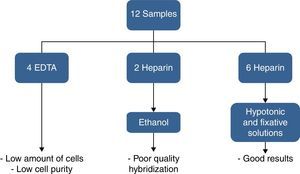
ResultsOf the twelve bone marrow samples used in this validation test, four were collected in EDTA and eight in heparin sodium. Bone marrow samples collected in EDTA resulted in low purity after CD138+ selection and two samples in heparin sodium fixed in ethanol resulted in bad hybridization. Therefore, good results were obtained for only six samples collected in heparin sodium treated with hypotonic solution (KCl) and fixed in Carnoy's solution. These results are shown in Figure 6.
The number of PCs detected by morphology on bone marrow aspirate slides (not the impure specimen) ranged from 1.2% to 82.8%. The median time from the sample arriving in the laboratory to the start of the process was 3h (range: 2–5h). After CD138+ selection, the sample purity ranged from 70 to 91%. A third analysis was performed for 40% of the probes, mainly to confirm atypical signals seen for the IgH probe.
Karyotype and iFISH results, described according to the standards of the International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (ISCN) 2013,17 are listed in Table 1.
Interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization and karyotype results from six samples.
| Sample | % of plasma cells in bone marrow aspirate (%) | % CD138+ cells after selection (%) | Karyotype | FISH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | 40.8 | 72.6 | 46,XX20 | Trisomy (total or partial) of chromosomes 1, 4, 11, 13, 17 |
| 8 | 22.0 | 70.4 | 46,XX20 | del(1p), del(16q) (MAF) |
| 9 | Not done | 90.9 | 46,XX20 | Monosomy 13, t(4;14) |
| 10 | 17.6 | 89.6 | 46,XY20 | 1q amplification, monosomy 13, t(4;14) |
| 11 | 4.80 | 70 | 44,X,-Y,add(1)(p34),add(5)(q11.2),del(6)(q23),-7, t(8;11)(q24;q13),-12,add(13)(p11.2),-14,-16,-18, +der(19)t(1;19)(q23;p13)x2,add(20)(p13),+2mar[2]/46,XY[18] | Extra copies of CDKN2C, CKS1B, P53 and FGFR3 |
| 12 | 1.20 | 70 | 46,XX20 | Normal |
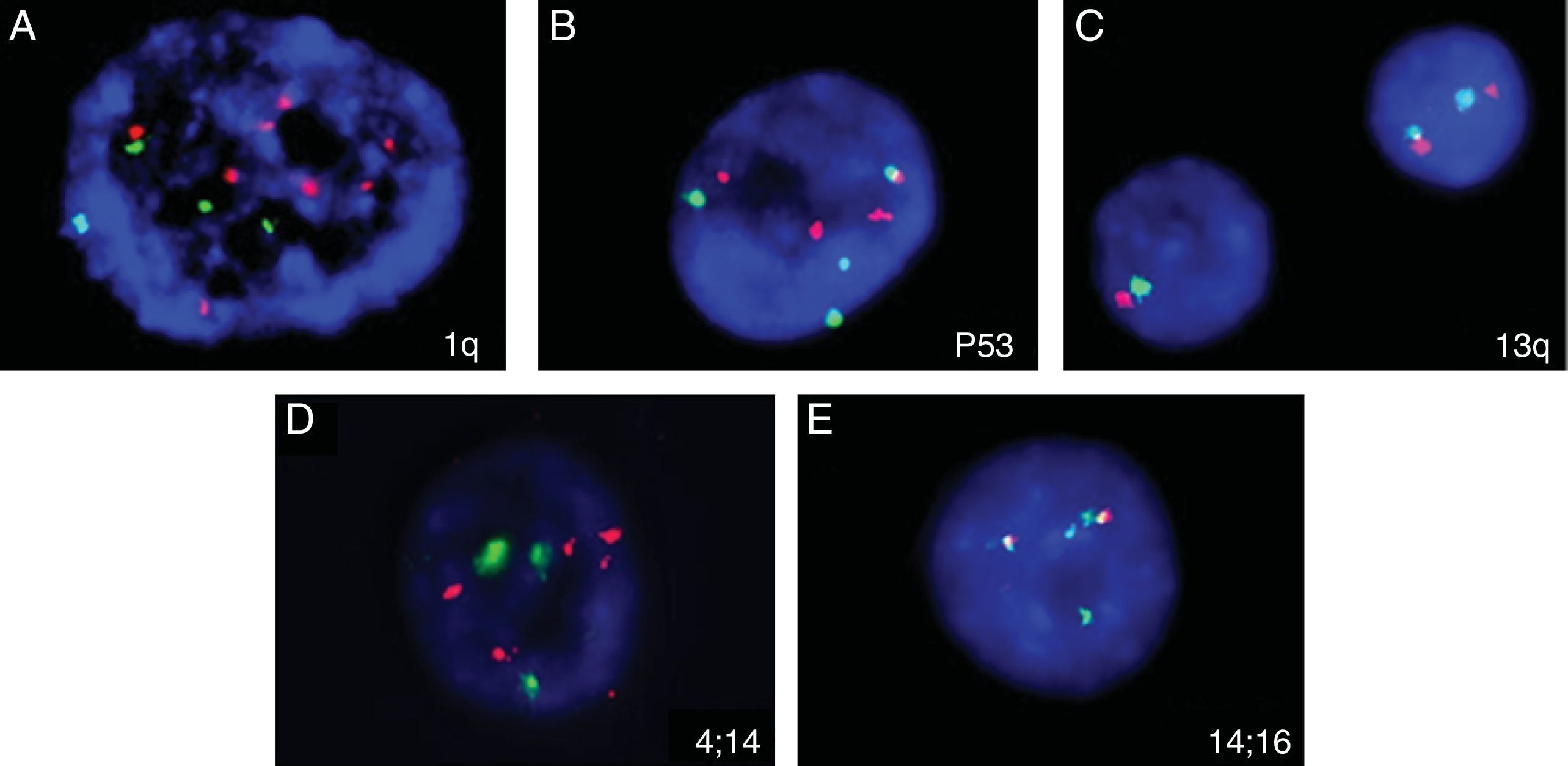
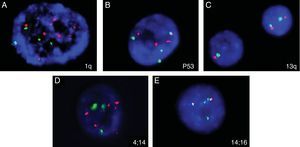
Five of the six cases analyzed showed abnormal findings in iFISH (Figure 7). Only one case (Sample 11) had abnormalities found by both karyotyping (Figure 8) and iFISH. Both t(4;14) and monosomy 13 were detected in two cases. Extra copies of genes and abnormalities on chromosome 1 were also identified.
Abnormalities found in five analyzed samples using the iFISH technique for multiple myeloma. (A) 1q amplification (several red signals); (B) trisomy 17 (3 red and 3 green signals); (C) deletion/monosomy 13q (only one red and one green signal in one nucleus); (D) 4 red and 4 green signals, suggesting extra copies of chromosomes 4 and 14; (E) t(14:16): 1 red, 1 green and 2 fusion signals.
A number of different genomic abnormalities are associated with MM. However, their detection by karyotyping and FISH can be limited due to the low proliferative rate of the PCs and the percentage of clonal cells in the specimen, respectively. Abnormal karyotypes are found in 20–50% of patients with MM; this rate can be even lower when MM is analyzed at diagnosis.6,7 Karyotypes can show numerical and structural aberrations with the most frequent numerical abnormalities described being hyperdiploidy in 61–68% of patients, pseudodiploidy in 9–20% and hypodiploidy, monosomy 13 and trisomy or tetrasomy of chromosome 9 in 10–30%. Concerning non-random structural aberrations, 14q32 translocations and aberrations of chromosome 1 are found in 30% and 40–50% of cases with abnormal karyotypes, respectively. The results of cytogenetic studies can be improved using longer culture periods (72h) and adding stimulating agents such as 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA or phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate) and cytokines (interleukin 6 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor).7
The selection of PCs for iFISH analysis improved the detection of genetic aberrations in MM. Different methods are described for targeting the PCs for iFISH analysis. One is performed in unpurified specimens: the analysis is carried out using only large mononuclear cells. This method results in low sensitivity, and involves a long time to train analysts to recognize the PCs, a prolonged analysis time, a certain degree of subjectivity and lack of reproducibility.5 The second is the CIg-FISH technique. This analysis is performed on monotypic PCs recognized by immunofluorescence-labeled light chain antibodies.15 This technique, which also requires a long time for training and does not have good reproducibility, was used in two Brazilian studies.18,19 The third approach is by selecting cells either by flow cytometry or immunomagnetic bead-based PC sorting.4
The current study followed the third approach using the magnetic cell sorting (MACS) technique giving the impression that this method is possible as a routine laboratory test if some precautions are taken. The magnetic cell sorting must be performed within a few hours. Hartmann et al.5 reported a time dependence for PC enrichment: the percentage of PCs in the enriched population decreased significantly with the age of the specimen. This phenomenon is due to the rapid loss of the CD138 marker on PCs after the cells are taken out of the bone marrow20; slides are stable and can be stored for a longer time before the iFISH procedure.
The panel probes herein selected were based on the EMN consensus. 1q amplification, t(4;14), t(14;16) and 17p13 deletion are associated with bad prognoses,4,8,12,21 and the 13q deletion is still controversial.18 In particular, t(4;14)(p16;q32) at diagnosis has been shown as a bad prognostic marker,18 even in smoldering MM22,23 and in patients with symptomatic MM treated with conventional chemotherapy, which may be ameliorated with bortezomib-based combinations.2
Another important issue is the cut-off levels for FISH probes. Some authors use statistical analysis (B-inv function, average and standard deviation) of normal control cases to determine the cut-off levels. However, to select PCs from normal bone marrow is very difficult. This study used the consensus cut-off levels defined by the iFISH myeloma workshop: 10% for fusion or breakapart probes and 20% for numerical abnormalities.4 Nevertheless, in general, bad prognosis is associated with a higher positivity such as 30% for del(13q) and 50% for del(17q).
Although the ENM guidelines suggest that a single experienced analyst is considered enough in specialist laboratories, this study was performed by two technicians (50 cells each). A good reproducibility was obtained, but in some doubtful cases, an extra analysis by a third analyst was necessary.
Although only six cases were used in this validation, a high rate of abnormalities (83.3%) was seen including two cases of t(4;14), which are markers of a bad prognosis; these cases would not have been identified if only conventional karyotyping was performed as both had normal karyotype results. This is higher than our historical detection rate of 34% abnormalities from 2007 to 2014, when samples were sent to a reference laboratory that performed FISH analysis for MM without PC selection (data not shown, personal communication).
Selection of PCs by MACS can also be an important tool for studying the genetic profile of MM with novel methods such as microarray-based comparative genomic hybridization (array-CGH), multiplex ligation dependent probe amplification (MLPA) and massively parallel sequencing, although the clinical relevance of these methods still needs to be better established.24–26
ConclusionIn summary, the iFISH technique using PC sorting with MACS is effective, has a good turnaround time and good reproducibility. The test was validated and established in the laboratory routine. In addition, this kind of cell sorting provides a pure PC population that suitable for other molecular and genomic studies.
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare no conflicts of interest.
We thank Nydia Bacal, MD and the biologists of the laboratory of Cytometry and Cytogenetics of Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein for their excellent technical assistance.


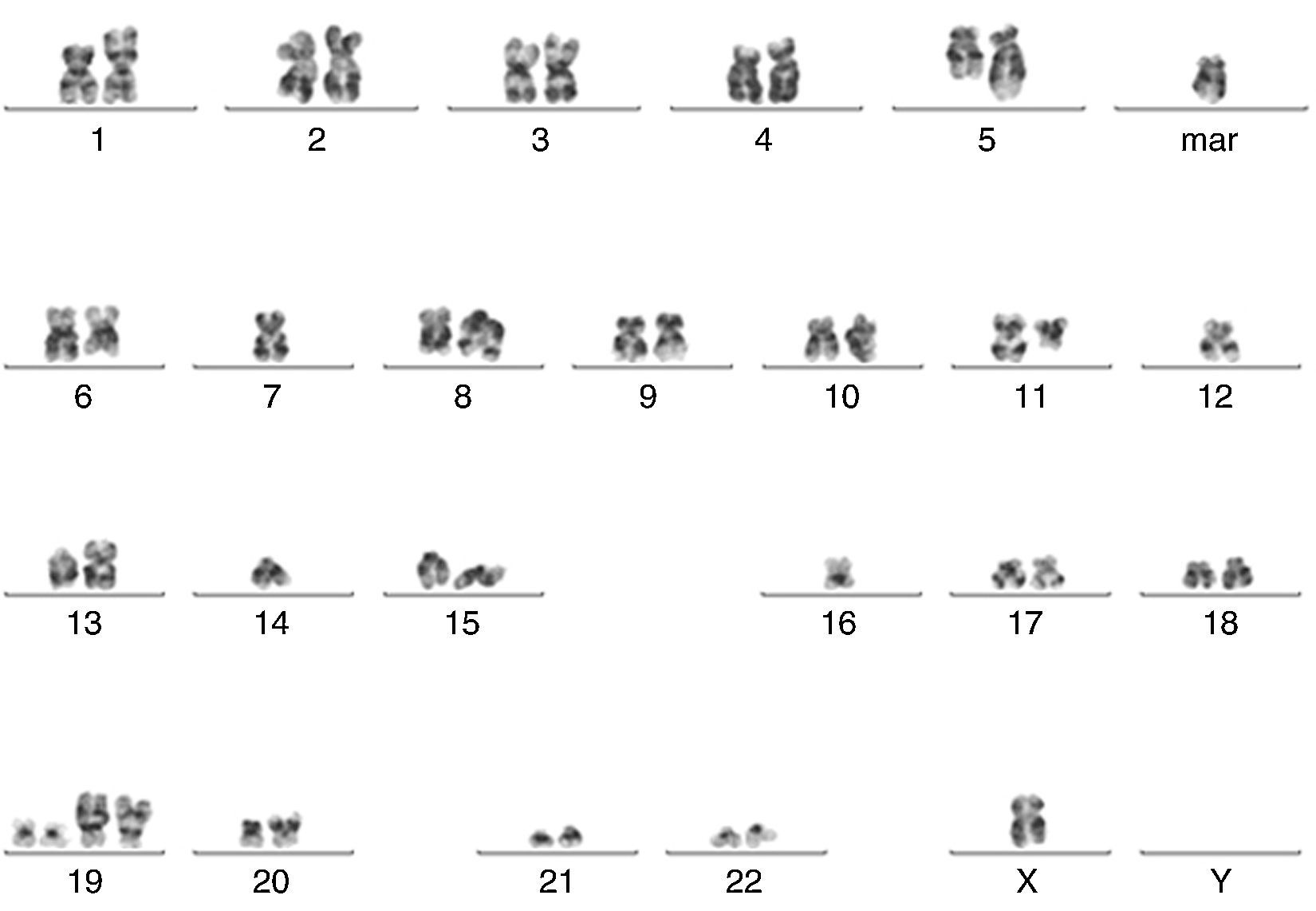
![Abnormal metaphase (Sample 11) showing several abnormalities (44,X,-Y,add(1)(p34),add(5)(q11.2),del(6)(q23),-7, t(8;11)(q24;q13),-12,add(13)(p11.2),-14,-16,-18, +der(19)t(1;19)(q23;p13)x2,add(20)(p13),+2mar[2]/46,XY[18]). Abnormal metaphase (Sample 11) showing several abnormalities (44,X,-Y,add(1)(p34),add(5)(q11.2),del(6)(q23),-7, t(8;11)(q24;q13),-12,add(13)(p11.2),-14,-16,-18, +der(19)t(1;19)(q23;p13)x2,add(20)(p13),+2mar[2]/46,XY[18]).](https://static.elsevier.es/multimedia/15168484/0000003800000002/v2_201605230808/S1516848416000086/v2_201605230808/en/main.assets/thumbnail/gr8.jpeg?xkr=ue/ImdikoIMrsJoerZ+w93OM6WmS6o9DeZl+SVh74uo=)





